For approximately 40 years, botulinum toxin has been used to treat various neuromuscular disorders, but it is not without risk. After all, the risk is in the name (botulinum toxin) and is often enough to make providers and patients wary of tapping into the therapeutic benefits of botulinum toxin. In this article, we will share the most important things pharmacists should know about BOTOX® injections to help you and your patients feel more comfortable with this therapy.
Source of BOTOX® and Mechanism of Action
The active ingredient in BOTOX® is onabotulinumtoxinA, an exotoxin produced by Clostridium botulinum, a spore-forming anaerobic bacillus. This bacterium produces seven distinct neurotoxins, but neurotoxin A is used most often clinically. In humans, onabotulinumtoxinA interacts with the presynaptic membrane of the neuromuscular junction to cause denervation by preventing the calcium-dependent release of acetylcholine into the synapse. Acetylcholine is an important neurotransmitter for muscle contraction, and by reducing the levels of available acetylcholine, we can treat a variety of neuromuscular conditions.
Medical and Cosmetic Indications
BOTOX® is FDA-approved for the treatment of several different medical conditions, including blepharospasm (involuntary eye blinking or twitching), cervical dystonia (involuntary muscle contractions in the neck), overactive bladder and urinary incontinence, severe axillary hyperhidrosis (increased underarm sweating), spasticity (stiff muscles), and strabismus (misalignment of the eyes). It may also be used for migraine prophylaxis.
BOTOX® Cosmetic is also FDA-approved for the treatment of three cosmetic conditions: moderate to severe forehead lines, frown lines, and crow’s feet.
An important distinction between the use of onabotulinumtoxinA for therapeutic and cosmetic purposes lies in its brand name. When used for medical conditions, onabotulinumtoxinA is branded as BOTOX®, but when used for cosmetic conditions, it’s termed BOTOX® Cosmetic.
Dosage, Preparation, and Administration
For all indications, BOTOX® is administered as an injection to the affected area – the muscle or dermis. However, the dosage and the time between treatments vary by indication, as noted in Table 1. Regardless of indication, the cumulative dose of onabotulinumtoxinA for adult patients should not exceed 400 units in a 3-month period.
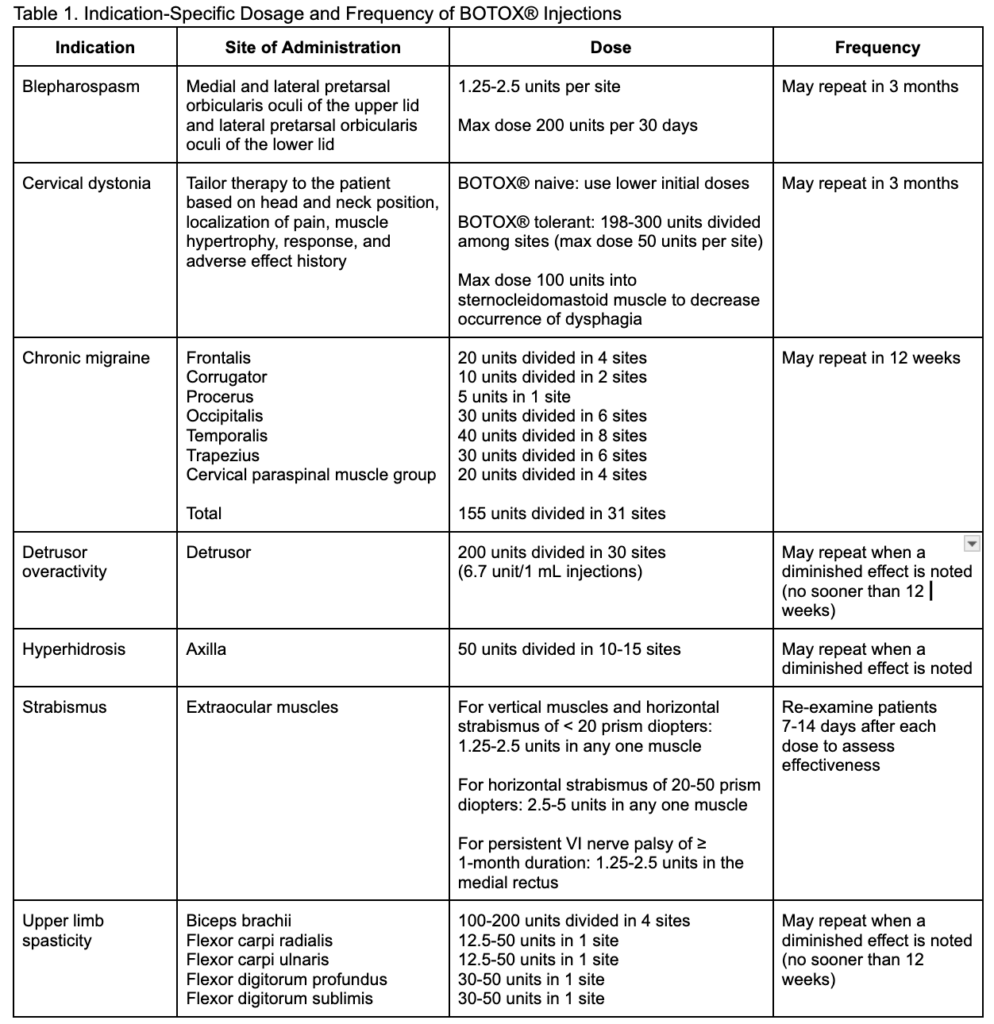
BOTOX® is supplied as an Injection Powder for Solution that must be reconstituted before administration, and providers must feel confident about preparing this product. The product must only be diluted with preservative-free 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP as shown in Table 2. After reconstitution, the BOTOX® product may be used immediately or refrigerated for up to 24 hours. Each BOTOX® vial is for single-use only, and any remaining reconstituted product should be discarded after 24 hours. It’s also important to note that botulinum toxin products are not interchangeable, so the dose units of one product cannot be converted or compared to another.
Table 2. Directions for Proper Reconstitution of BOTOX® Vials
Common and Serious Adverse Effects
Adverse effects also vary based on the indication and the site of the BOTOX® injection. For bladder-related indications, some common side effects include urinary retention, urinary tract infection, and dysuria. Dysphagia, headache, neck and back pain, upper respiratory infection, and flu-like symptoms are possible with the treatment of cervical dystonia. For all indications, injection site pain is common.
More serious adverse reactions include dysphagia, aspiration pneumonia, and excessive weakness. These adverse effects are more common when a botulinum toxin product is administered for an unapproved use.
BOTOX® holds a Black Box Warning for the distant spread of toxin effect, in which symptoms consistent with botulinum toxin are noted distant from the injection site. These symptoms include asthenia, generalized muscle weakness, diplopia, ptosis, dysphagia, dysphonia, dysarthria, urinary incontinence, and breathing difficulties – some of which may be fatal.
Contraindications, Precautions, and Drug Interactions
BOTOX® is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any botulinum toxin product or any components in the formulation. Serious hypersensitivity reactions may present as anaphylaxis, serum sickness, urticaria, soft-tissue edema, and dyspnea and require discontinuation of the medication and immediate medical assistance.
It is also contraindicated in patients who have an infection at the site(s) of administration.
BOTOX® injections should be used with caution in patients who have comorbid conditions that may be exacerbated by BOTOX®, such as pre-existing neuromuscular disorders (e.g., myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton syndrome), swallowing or breathing difficulties, or compromised airways or respiratory statuses. Though the BOTOX® package insert does not specifically mention asthma or COPD as conditions limiting the use of BOTOX®, it does refer to the results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study in which patients with stable reduced pulmonary function (defined as FEV1 40-80% of predicted value and FEV1/FVC ≤ 0.75) treated with BOTOX® experienced a greater decrease in Forced Vital Capacity compared to patients treated with placebo. However, this difference was not statistically significant. Interestingly, there is a prospective, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial currently in process to assess the safety and efficacy of BOTOX® for the therapeutic management of patients with moderate COPD. More to come!
As for drug interactions, the effects of onabotulinumtoxinA may be potentiated with the concomitant administration of other agents that interfere with neuromuscular transmission, including aminoglycosides and anticholinergic agents. Extreme weakness may also be exacerbated by the combination of onabotulinumtoxinA and other muscle relaxants.
This article was written by Kaitlyn Nichols, PharmD Candidate in collaboration with Eric Christianson, PharmD, BCPS, BCGP
Popular Amazon Books
- 30 medication mistakes PDF
- 18+ Page Drug Interaction PDF
- 10 Commandments of Polypharmacy Webinar based on my experiences in clinical practice
References:
- BOTOX® (onabotulinumtoxinA) [package insert]. Madison, NJ: Allergan Pharmaceuticals Ireland a subsidiary of: Allergan, Inc.; 2023.
- OnabotulinumtoxinA [Contained in: Botox], IBM Micromedex® DrugPoint Summary (electronic version). IBM Watson Health, Greenwood Village, Colorado, USA. Available at: https://www-micromedexsolutions-com.ezp3.lib.umn.edu (accessed: April 1, 2024).







0 Comments